Many types of documents are used in international transport. One of them is a TIR carnet – an international customs document used when moving goods between at least two customs territories.
TIR carnet
Usually, under the TIR procedure, the goods are sealed by the customs authorities where the load or a part load of goods shipment begins. They are carried by means of vehicles and containers (movable tank, lift-van, or other similar structure) by road, following the Convention on the international transport of goods under cover of TIR carnets (TIR Convention, in French Transport International Routier – International Road Transport). Vehicles carrying out a TIR transport have a rectangular plate with the “TIR” inscription affixed.
The TIR carnet simplifies the procedures at the customs border and in customs offices for road traffic. While en route, there is no obligation to pay additional charges (security or guarantees) at Customs offices. The entire border crossing procedure is also much shorter as the cargo does not undergo examinations. Under the TIR Convention, however, the customs authorities have the right to examine the goods.
Moreover, the TIR carnet enables goods to be transported within an international transit regime with a minimum of interference by customs administrations en route and serves as a guarantee. It is issued by an authorized guaranteeing association established within the customs territory. The individual guarantee vouchers cover an amount of EUR 10 000 (in the Member States of the European Union).
Goods moved under TIR carnet
The TIR carnet is used for almost all types of cargo. Tobacco products and alcohol are excluded from such transport, although wine, beer, and raw tobacco for further processing are allowed. In that case, the TIR carnets must be clearly marked “TABAC/ALCOOL” or “TOBACCO/ALCOHOL” on the cover and all vouchers.
For the transport of bulky or heavy goods, a special indication on the voucher: “HEAVY OR BULKY GOODS” or “marchandises pondéreuses ou volumineuses” in bold is used. Such goods are carried by means of a non-closed vehicle or container.
The transported goods are sealed (containers or vehicles) by the Customs office of departure. If it is necessary to transship the goods, a customs authority drawing up the report must be present during the transshipment.
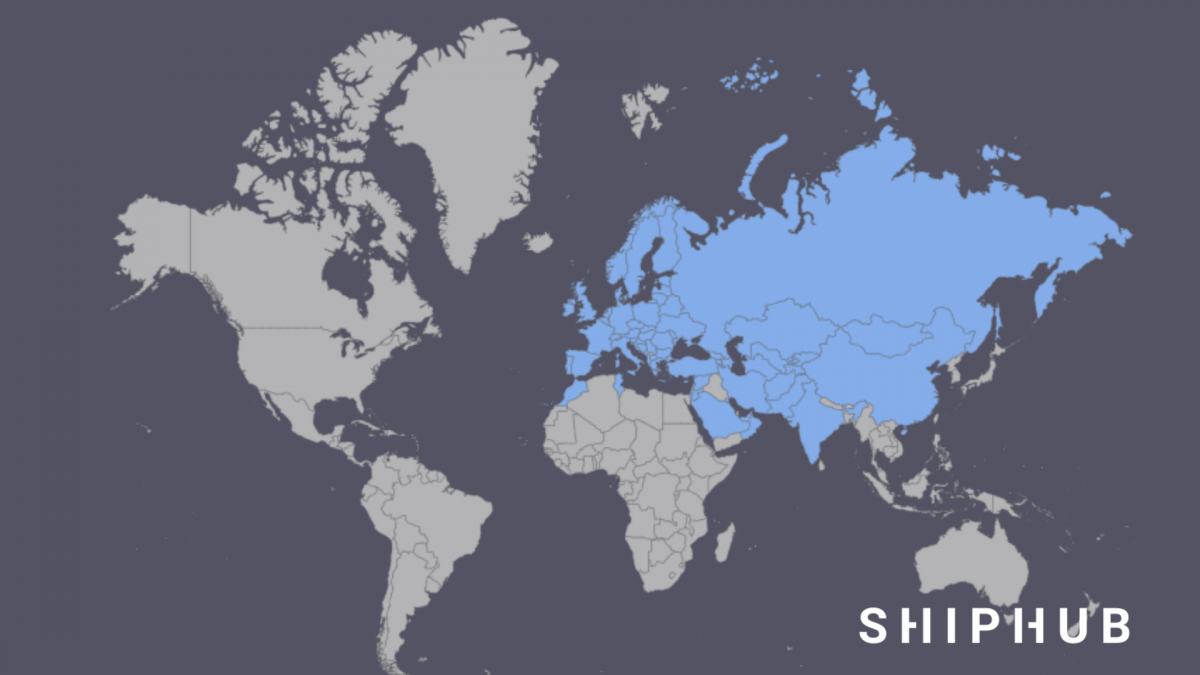
Which countries use the TIR carnet?
There are 75 parties to the TIR Convention. The TIR carnet can be used in every European country, as well as in some African and Asian countries and the Middle East. The United States of America, Canada, Chile, and Uruguay are also parties, although TIR carnets are not used in these countries.
The goods must be moved between customs territory for the TIR procedure to apply. Therefore, the TIR carnet is not applicable in the event of transport between EU countries. However, if the goods are moved through a third country’s territory applying the TIR procedure, the carnet is valid. Thus, it applies when you import, or dispatch goods from outside the EU to an EU country or the load passes through a country that is not an EU Member State.
Countries with which a TIR transit operation can be established:
- Afghanistan
- Albania
- Armenia
- Austria
- Azerbaijan
- Belarus
- Belgium
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Bulgaria
- China
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Georgia
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- India
- Iran (the Islamic Republic of)
- Ireland
- Israel
- Italy
- Jordan
- Kazakhstan
- Kuwait
- Kyrgyzstan
- Latvia
- Lebanon
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Malta
- Moldova
- Mongolia
- Montenegro
- Morocco
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Oman
- North Macedonia
- Pakistan
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Russian Federation
- Saudi Arabia
- Serbia
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Syrian Arab Republic
- Tajikistan
- Tunisia
- Turkey
- Turkmenistan
- Ukraine
- United Arab Emirates
- United Kingdom
- Uzbekistan.
How to obtain the TIR carnet?
TIR carnets are owned by International Road Transport Union – IRU and printed in Geneva. Each of the TIR carnets is printed on a special paper and has a number of safeguards; therefore, it is relatively easy to spot false documents. Each of TIR carnets printouts has a TIR identification number, barcode, and a watermark.
Authorized national road transport associations issue TIR carnets. The documents are valid internationally.
You must apply to the association to receive access to the TIR procedure. The association may demand that you provide certain information regarding your company, namely registration, ownership, direction, and shareholding.
An authorized TIR carnet holder’s status requires that the minimum conditions and requirements imposed by the TIR Convention, the national legislation, and the Associations’ rules are permanently met.
TIR Convention, Article 6 and Annex 9, Part II on Minimum Conditions and Requirements for Holders states that holders of TIR carnet must:
- prove experience or, at least, the capability to engage in regular international transport in regular international transport
- sound financial standing
- prove knowledge in the application of the TIR Convention
- prove an absence of serious or repeated offenses against Customs or tax legislation.
Moreover, the holder is required to lodge guarantees, such as:
- “admission” guarantee (in the form of a cash deposit, bank guarantee, or a Letter of Guarantee)
- special guarantees to cover claims lodged against the guarantee chain
- guarantees related to unreturned TIR
- additional guarantees in other situations.
When you already have the TIR carnet, you are responsible for payment of all duties, taxes, fines, and penalties relating to a TIR transport.
What does the TIR carnet consist of?
The TIR carnet is printed in French (the cover also in English). It consists of a cover, a yellow goods’ manifest, and vouchers in pairs: one white and one green. Some of the parts are intended to be torn out.
The TIR Carnet Holder established in the EU is obliged to register it in the Community electronic system NCTS.
The boxes are completed as it follows:
- when issuing the carnet, the association completes boxes 1-5 on the cover
- the carrier completes boxes 6-12 on the cover and boxes 2-15 on all volets and the manifest before commencing the journey
- the authorities at the customs office of departure complete boxes 16-23 and 1-6 on counterfoil No. 1
- the authorities at the customs office of destination complete boxes 24-28 and 1-6 on counterfoil No. 2.
There are several types of TIR carnet:
- 4-volet (journey between two customs territories)
- 4-volet-PILOT, applicable from any EU country to a third country having a direct border with the EU, for example, Poland–Belarus and vice versa
- 6-volet (up to three customs territories)
- 6-volet-PILOT for transport from or to a country of the European Union or from a third country to a third country, with transit through any EU country (Switzerland–Belarus; Turkey–Ukraine, etc. through the EU customs territory)
- 14-volet (up to seven customs territories)
- 20 volets.
Volet is a pair of documents fastened with a cover. There is one pair per customs border. All volets must be completed.
The prices and the list of associations issuing TIR carnets in individual countries around the world are available in the UNECE document. The websites of associations in EU countries are available on the official site of the European Commission.

Rules for using the carnet
- customs clearance is carried out at the Customs offices of departure and destination
- in the case of undertaking TIR transport to/from/through the European Union territory, obtain an EORI number and mention it in box 4 of voucher 1 and 2 used for the TIR operation on the territory of the European Union
- valid for one-time-only, by an appropriately sealed vehicle or container
- the TIR carnet is valid only for a specified period; alternation is forbidden
- do not present the TIR carnet with an overdue validity date to a Customs Office of departure
- complete all volets, regardless of whether they will be used or not
- it is forbidden to transmit the TIR carnet to a third party
- you must return all used and unused TIR Carnets as quickly as possible
- for at least five years, keep a record of all TIR Carnets issued to you and the details of all journeys on which a TIR Carnets is used
- alternations to the completed boxes are forbidden unless approved by competent authorities
- in the event of destruction or damage to the goods en route, the carrier reports the fact to the nearest customs authorities to make an official report of the incident
- a vehicle with the affixed TIR plate must meet the technical requirements confirmed by a customs certificate (valid for two years)
- during transport, possible duties and taxes should be secured with international guarantees.
Legislations
The most important legal texts concerning the TIR carnet are:
- The Customs Convention on the International Transport of Goods under Cover of TIR Carnets (TIR Convention, 1975)
- 2009/477/EC: Council Decision publishing in consolidated form the text of the Customs Convention on the international transport of goods under cover of TIR carnets (TIR Convention)
- Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2015/2447 laying down detailed rules for implementing certain provisions of Regulation (EU) No 952/2013 of the European Parliament and of the Council laying down the Union Customs Code
Read about another international customs document – ATA carnet.

