Fumigation is a process of exterminating living organisms. In particular, it refers to pests that hollow the tubules in the wooden material and nest in them, and then along with the load are transferred to other parts of the world.
Fumigation in shipping – What is it?
The fumigation process helps to get rid of pests. Insects are one of the largest medium of diseases, so we should pay special attention to epidemiological protection in international transport. General import-export regulations usually impose the fumigation process.
Fumigation consists in drying wood at 56°C for 30 minutes, as well as on decontamination with heavy gas (a compound that, after spraying, does not float in the air but falls to the ground). The gas penetrates through the cracks in the wood and gets rid of all living organisms.
It is primarily aimed at reducing the risk of spreading quarantine pests in international trade.
Export fumigation
Fumigation used in international transport is often referred to as export fumigation, international fumigation or sanitary fumigation.
Fumigation in shipping – When is it required?
Fumigation is used not only for international transport but also for the preparation of packaging for storage of various consumer products. Repeated use of the same packaging makes them susceptible to pest attacks. In this case, it is recommended to periodically clean all types of crates, pallets, boxes, boxes with wooden partitions and floor, as well as other such places.
In international transport, the process of fumigation of wood is a basic condition for passing through customs clearance and admission to transport.
Fumigation is required for international transport outside the European Union and between certain member countries (including Portugal, Spain).
On the other hand, packaging made of wood-based materials, which are made by pressing under pressure, with the addition of synthetic adhesives doesn’t require purification.
Export fumigation is not required in every direction, while countries such as the US, China, or Australia must fumigate.
ISPM 15 Standard
Fumigation works are carried out under the supervision of the State Plant Protection Service, following the International Standard for Phytosanitary Measures ISPM number 15 of the International IPPC Convention on Plant Protection (abbreviated as IPPC ISPM 15: 2009).
The ISPM 15 standard is used in countries outside the European Union. It describes the method of treatment of wooden packaging, guaranteeing the liquidation of all potentially harmful organisms.
Fumigation of food transported by containers
It also happens that fumigation is subjected to food transported internationally. Methyl bromide has been used in the past, but it is currently prohibited in the European Union. However, outside of the EU (including India), you can still encounter such methods. An interesting alternative currently used in many countries is cooling.
Protection against pests
After the fumigation process, wooden packaging remains a safe means of transport, completely free from the presence of various types of insects.
Fumigation is undoubtedly a fast and effective process and, moreover, it does not have a negative impact on the disinfected goods.
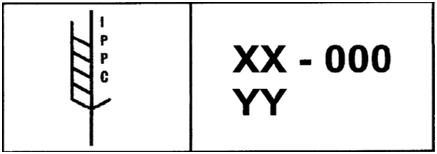
Mark
On wooden elements, after the process, a special IPPC logo is applied.
XX – determines the ISO code.
000 – the number assigned by the National Plant Protection Organization.
YY, on the other hand, means information on how to protect the timber and can be presented in the following way:
- DB (debarked) – the wood has been subjected to mechanical treatment removing the remains of the bark
- MB (methyl bromide) – the wood was decontaminated by gassing with methyl bromide
- HT (heat treatment) – the wood that was used to build the packaging was dried in a chamber at a high, well-defined temperature for the right time
The mark or simply a stamp must comply with the provisions of ISPM 15 and should be on each wooden package or pallet.
The label should contain the logo of the company making the fumigation, the code of the producer of the preparation, the method of treatment which the wood was subjected to and the symbol of the country where the fumigation was made.
Consequences
Goods that have not been subjected to the process of fumigation will certainly not be introduced into the country that requires such a process.
Besides, such goods may be subject to additional charges or withdrawn to the country of dispatch at the expense of the exporter.
In the case of groupage consignments consolidated in one container, when one packaging has not passed the fumigation process, the goods from the whole container are stopped, and no one from the importers can pick up their shipment.
Alternatively, in such a case, a fumigation process can be carried out in the country to which the parcel was sent; however, it is a long and costly procedure. It is subjected to the entire contents of the container, which can lead to the destruction of transported products. In the case of importing food products, this option is not even considered.