Germany is Europe’s largest importer of products from the US, with 53 billion dollars in exports over the last twenty years. The two countries are very well-connected, and if you are interested in importing products, you need to know the process well. Here, you will find all the basics of shipping from the US to Germany.
How can you ship goods from the US to Germany?
There are two shipping methods from the United States to Germany: air and ocean. Both options have advantages and disadvantages, and each is intended for specific types of cargo.
Ocean shipping from the US to Germany
This method is usually recommended for larger shipments. Its main disadvantage is the longer transit time – but this comes with a lower price. Sea freight also has two forms of transport: LCL and FCL shipping.
LCL (Less Than Container Load) is recommended for smaller shipments. In LCL mode, you must share container space with others, which also means a reduced price. LCL’s main disadvantage is that it might take longer to arrive than anticipated, so it is not recommended if you are short of time.
FCL (Full Container Load) mode is better for larger shipments, as you rent an entire container for just your cargo. It takes a shorter time than LCL and is recommended if the shipment must arrive by a given date.
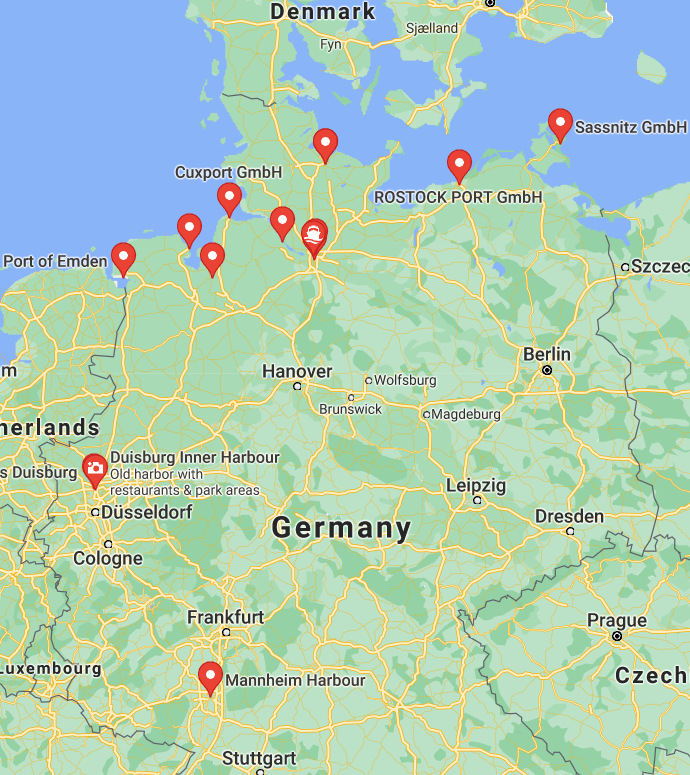
Seaports in Germany
Major seaports in Germany are in Hamburg, Bremen, and Wilhelmshaven. Hamburg is among the largest ports in Europe. After the cargo arrives at the port, it will be sent to its destination by rail or truck.
Here are some examples of how long shipping between the US and Germany takes:
- Baltimore to Hamburg – 15 days FCL
- Charleston to Hamburg – 23 days LCL
- New York to Hamburg – 14 days FCL
Airfreight from the US to Germany
Airfreight is always the quickest option – at the same time, however, it costs significantly more than ocean shipping. It is recommended if the cargo needs to arrive quickly or has a short shelf-life. Airfreight is also a good choice for high-value goods because of better security at airports. The cargo should not take more than four pallets, as bigger shipments will not be worth the high price.
Germany is home to the largest cargo-handling airport in Europe: Frankfurt Airport. It handles as much as two million tons of cargo each year. The favorable location makes importing products to Germany by air much easier and faster. Other cargo airports in the country are in Berlin, Munich, and Hamburg. Here are some examples of the transit time of cargo shipped from the United States to Germany:
- Atlanta or San Francisco to Frankfurt – 6 days
- Denver or Los Angeles to Frankfurt – 8 days
- New York to Frankfurt – 5 days
German customs
As in other EU countries, Germany requires the importer to present a list of documents before allowing foreign goods into the country. These are
- commercial invoice
- letter of credit (or other payment terms the parties agreed on)
- packing list
- certificate of origin
- bill of lading for ocean freight or the air waybill for airfreight.
Although there are not many restrictions when importing to Germany, some products fall under additional regulations. Among them are medicinal products, chemicals, steel and iron products, clothing and textiles, and vegetables and fruits. More specific information for these and other products can be found in the TARIC database.
How much does shipping from the US to Germany cost?
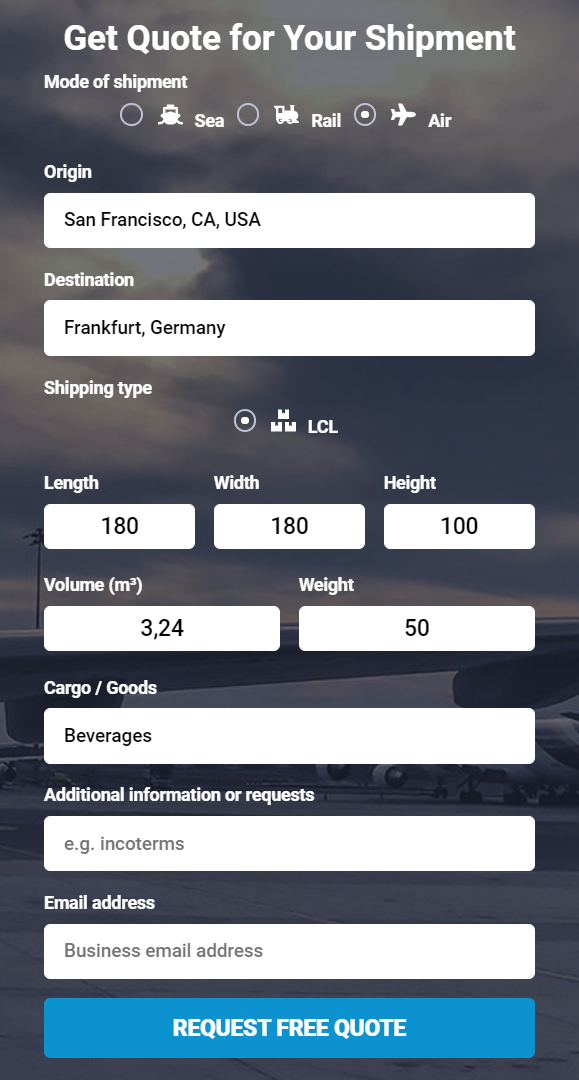
The total cost always depends on multiple factors – whether you choose air or sea shipping and the specifics of the cargo. To see a quote for your shipment, you can fill out a form here on ShipHub. Below you can find examples of such forms:

International Trade between the United States and Germany is highly beneficial and will surely stay that way for many years to come. To import products from the US to a European country, all the importer has to do is familiarize themselves with all the forms of transport and necessary steps, as well as German customs. Thanks to easily accessible technology, doing it is simpler than ever before.
Read our other guides on shipping to Germany:






